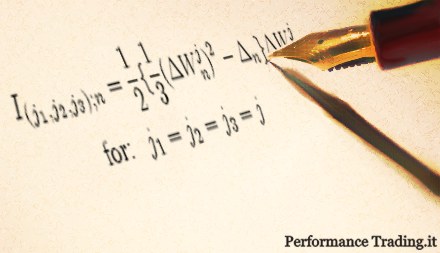Performance Trading
Your Source For Finance Education
Indice dei documenti su: Modelli Econometrici

Lo sviluppo di questa tesi è una diretta conseguenza dell’esperienza maturatadurante lo stage presso un’ ente che si occupa di previsioni finanziarie, nonché di un costante scambio di informazioni via e-mail con l’autore del libro “Expert Trading System: Modeling Financial Markets with Kernel Regression”.La tesi tratta la descrizione e lo studio di fattibilità di una metodo di regressione non parametrica, la kernel regression, applicata alla previsione intraday dei valori del Fib30.
Indice VIX, Volatilità, Modelli e Analisi Empirica/AT/Combinazione/cprIndex.htm/a
La ricerca e l’analisi di relazioni tra la volatilità dei prezzi degli strumenti finanziari e il
loro rendimento è stata ed è tutt’oggi al centro di grande attenzione da parte degli
studiosi di econometria, finanza e statistica. Uno dei principali interrogativi riguarda la
previsione del rischio legato all’andamento globale dell’economia e dei mercati sulla
base dell’informazione disponibile (la storia passata).

GRETA, Venezia. Una versione dell'articolo è pubblicata nel volume a cura di D. Sartore, Gli strumenti derivati, IPSOA,1999.

Una versione dell'articolo è pubblicata nel volume a cura di D. Sartore,
Gli strumenti derivati, IPSOA, 1999.
Una versione dell'articolo è pubblicata nel volume a cura di D. Sartore, Gli strumenti derivati, IPSOA,1999.

Metodologia per affrontare il problema di "previsione del mercato" si tratta di una delle assunzioni chiave per molti esercizi di pianificazione finanziaria e budgeting e gestione proattiva del rischio finanziario.

This paper aims to pursue two closely connected purposes. The first is to provide a
theoretical framework, based on coherence constraints, for a technique of multicriteria
analysis that allows to convert a partial pre-order into a total pre-order. The second it to
show the possibility of measuring statistically the amount of modification implicitly made
to the evaluations concretely expressed in the binary comparisons in order to make them
coherent. This information may be useful both to the decision-maker who may wish to
redefine certain evaluation criteria, and to the user of the ranking obtained with the
multicriteria method, in order to determine its reliability.
Based on the Partial Distribution, we presents the concepts and expressions of DF process and
DF structure and put forward the DF structure models of pricing options on a non-dividend-paying underlying for the
first time. The DF structure models are able to price the call and put options exercised at any time, so it is applicable
to pricing the American and European options. Finally, examples are given to compare the options priced by DF
formulas and by Black-Scholes formulas, they show, as a whole, that the DF’ prices of options are closer to the
trading prices than Black-Scholes’ prices in many cases.Prof.

In tale articolo si valuta l’abilità del modello stocastico univariato di Cox,
Ingersoll e Ross di identificare titoli caratterizzati da mispricing, ovvero
caratterizzati da una condizione di sopravvalutazione (prezzo di mercato superiore
al prezzo equo) o di sottovalutazione (prezzo di mercato inferiore al prezzo equo), e
di fornire, conseguentemente, informazioni utili per il trading.

The paper investigates the influence and explanatory power of aggregate insiders trading
activities on momentum trading strategies. We find that insiders trading activities can predict
cross-sectional returns and can strengthen the naı¨ve momentum effects. The risk factors such
as size and BM cannot explain the strong momentum effects in our refined momentum
strategies. We interpret our findings as that the continuous overreaction causes the mediate
term momentum effects and over pricing. In the long term, these overly priced stocks will be
corrected with passing time. The correction of over pricing causes long-term reversals.
© 2002 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
We can estimate the market view using the volatility which is implied by
the market prices. Using real data from the market, we can simulate the asset
price path with its corresponding implied, local and stochastic volatility.
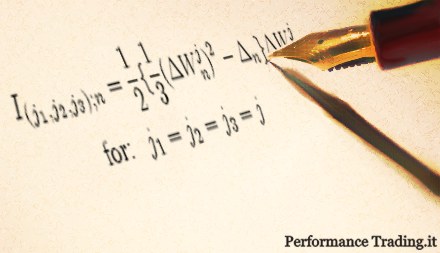
The purpose of this document is to introduce implied, local and stochastic volatility, to review
evidence of non-constant volatility, and to consider the implications for
option pricing of alternative random or stochastic volatility models. We focus
on continuous time diffusion models for the volatility, but we also briefly discuss
certain classes of discrete time models, such as ARV or ARCH.

We can price any financial instrument using Monte Carlo and the payoff. Another method of pricing is using the exact solution for its corresponding SDEs. This method requires formulas that are not always easy or possible to find. In this document, we present the corresponding approximations for both Euler and Milstein schemes for the usual Geometric Brownian Motion and the stochastic volatility models. Also, we present five methods of how we can simulate the double integrals for the 2 dimensional Milstein approximation.

In this paper we examine a different kind of technical indicator which suggests a structural relationship
between High, Low and Close prices of daily exchange rates. Since, for a given
exchange rate, it can be shown that these prices have different time series properties, it
is possible to explore the structural relationships between them using multivariate
cointegration methods.

I metodi di simulazione Monte Carlo si sono rivelati uno strumento efficace e computazionalmente flessibile per la risoluzione di problematiche di carattere finanziario.
We introduce a stochastic price model where, together with a random component, a moving average of logarithmic prices contributes to the price formation.

In this note, we aim to emphasize the mathematical tractability of the model by presenting analytical and numerical results comparable with the known ones in the classical Black-Scholes environment.

Lezioni di Econometria del Prof. Paolo Mattana Dipartimento di Economia
Università degli Studi di Cagliari
Notwithstanding its widespread use in financial markets and well-documented
profitability, technical analysis is still perceived to carry useless information. This
paper provides a possible explanation for this puzzle that goes beyond the
standard self-fulfilling prophecy argumentation. If at least some of the asset price
fundamentals are not currently observable, the oscillator model is able to infer
regime shifts in the process of these variables through past asset prices. From this
point of view, technical analysis can be interpreted as a cheap proxy for Bayesian
learning.
It is demonstrated in this paper that the exchange rate "overshoots the overshooting
equilibrium" when chartists are introduced into a sticky-price monetary model due originally
to Dornbusch (1976). Chartists are introduced since questionnaire surveys reveal that
currency trade to a large extent is based on technical trading, where moving averages is
the most commonly used technique.